Article: Why SPF Is Non-Negotiable for Every Skin Type

Why SPF Is Non-Negotiable for Every Skin Type
Once thought of as a concern almost exclusive to older generations, those with fair skin, or anyone who religiously (over) uses sunbeds, skin cancer is now on the rise across all demographics.
Despite significant advances in our understanding and awareness of the condition, dermatologists are witnessing a sharp increase in both melanoma and non-melanoma cases worldwide, even among celebrities who seemingly have access to the best care.
This can only mean that skin cancer does not discriminate, and as cases continue to climb, it's more important than ever to understand what's fueling this surge, who is most at risk, and crucially, how we can protect ourselves without compromising on quality time outdoors.
At SunsolveMD, our mission is to make daily sun protection a universal habit, not just a seasonal afterthought.
Here’s why SPF is non-negotiable for every skin type, and how you can protect yourself and those you love.
Understanding Skin Cancer: What You Need to Know
The first most important thing you must know about skin cancer is that it's the most common cancer in the United States and worldwide.
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, one in five Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70.
The second most important thing? Most cases are preventable.
However, before we jump to the part of teaching you a simple and efficient way to protect yourself, let's first talk a little bit about the different types or forms of skin cancer, what they look like, and how to differentiate them from other blemishes such as freckles, moles and tags which can often look menacing on your body.
The Different Types of Skin Cancer
There are three main types of skin cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):The most common form of skin cancer, and often considered the least dangerous, basal cell carcinoma appears as pink, red, pearly, or waxy bumps, with a translucent or shiny surface.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Often presents as red, scaly patches or sores that may crust or bleed.
Melanoma: The deadliest form, but less common, melanoma can develop anywhere on the body and often looks like a shapeless, borderless, and irregular mole that displays shades of pink, red, brown, black, or even blue. Melanoma can be either flat or raised, depending on the type and stage, and may change in size, shape, or appearance over time.
Understanding the distinct appearances of various skin cancer forms is crucial for preventing late diagnosis and ensuring early intervention, which in turn helps improve treatment outcomes.
Signs and Symptoms
Similarly to distinct appearances, the various forms of skin cancer often manifest unique signs and symptoms, such as new growths or subtle or noticeable changes in existing spots and moles.
Common warning signs and symptoms of skin cancer include:
- Persistent sores that do not heal, bleed, crust, or scab for weeks at a time.
- Changes in the color, size, or shape of a mole, particularly appearing to grow larger or changing from a clearly defined spot to one with irregular borders.
- Persistent itching, tenderness, and other uncomfortable sensations, such as pain, tightness, and the feeling of stretched skin.
- The development of a lump or bump that appears shiny, red, or pearly may be a sign of basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
- A rough or scaly red patch that may bleed or crust for longer periods could be squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
Apart from recognizing the potential development of skin cancer based on its obvious characteristics, pay attention to early symptoms, as this is another crucial component for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
What Causes Skin Cancer? UV Radiation & Other Risks
The primary cause of skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds.
Namely, two main processes are involved in the formation of skin cancer:
-
Direct DNA Damage from UV Radiation:
When UV rays penetrate the skin, their energy is absorbed by DNA molecules, causing abnormal distortions or lesions in the DNA helix. These lesions block DNA repair, leading to permanent mutations, often in critical tumor-suppressing genes such as TP53. When these genes malfunction, cells can grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that may grow into carcinomas.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as Key Contributors:
In addition to direct DNA mutations, UV exposure generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are unstable molecules that oxidize DNA bases and damage essential proteins involved in DNA repair. This oxidative stress further impairs the skin’s ability to recover, weakens immune defenses, and allows malignant cells to thrive and evade detection, accelerating the development and spread of skin cancer.
The takeaway? UV radiation doesn’t just cause mutations that result in malignant growths; it incapacitates the very systems designed to destroy them.
Who’s at Risk? (Spoiler: Everyone)
It’s a common misconception that only people of a certain age, skin color, or lifestyle habits need to worry about skin cancer.
However, in reality, anyone can get skin cancer, and the risk is increasing across all demographics.
Recent research shows that the incidence of skin cancer is rising among people under 50, as well as celebrities, highlighting the importance of prevention and early detection for everyone, not just older adults or those of a particular background.
However, anyone can develop skin cancer, certain factors can significantly increase the risk.
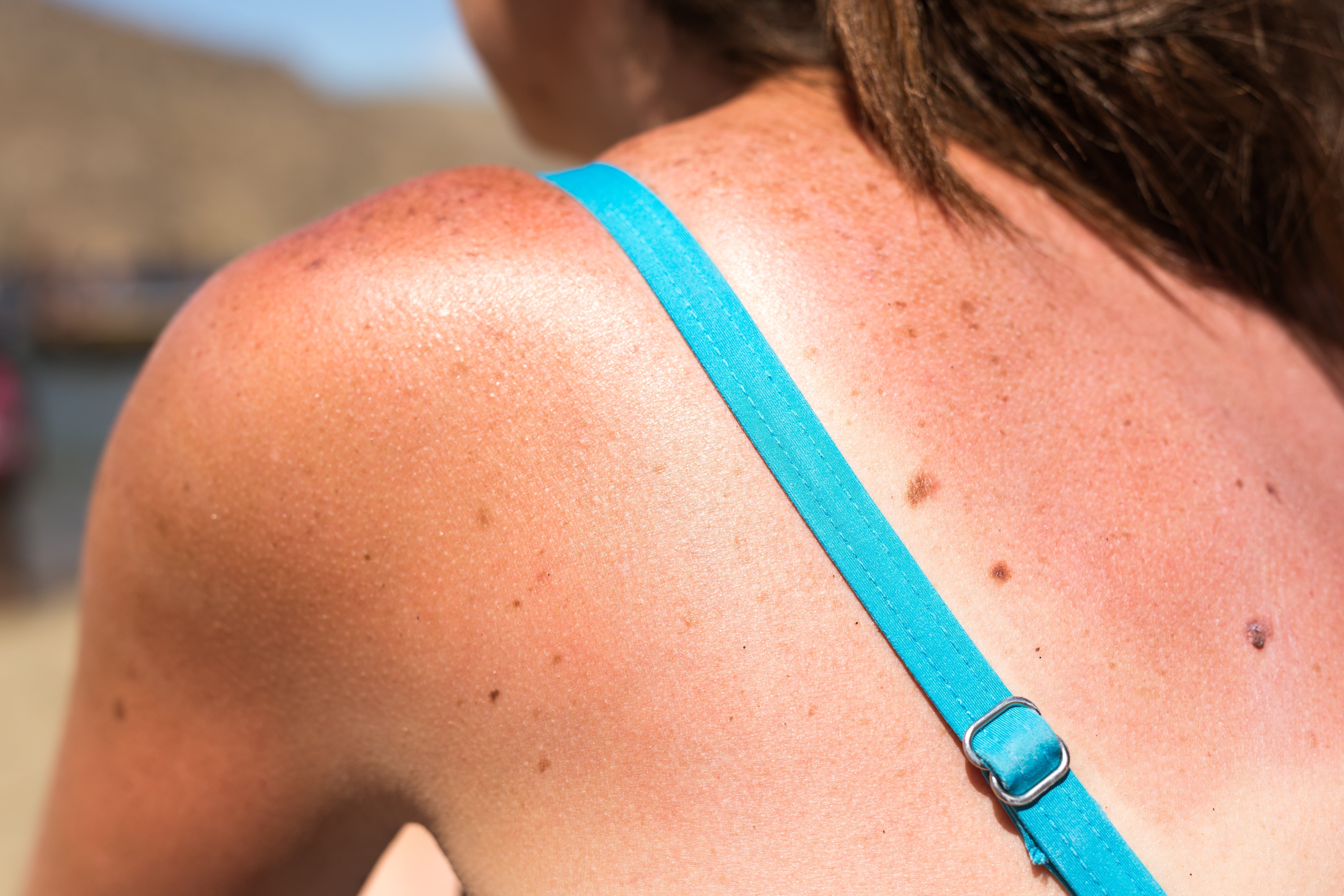
Lighter skin: With less melanin acting as a protective barrier, UV radiation can penetrate more easily into the skin, causing more DNA damage, and making individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes more susceptible to sunburns and, ultimately, skin cancer.
High mole count: Having a large number of moles increases the likelihood of cells undergoing malignant transformation. Some moles, especially atypical or irregular ones, are more prone to becoming melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer.
Family history: Some inherited genetic conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, characterized by extreme sensitivity to sunlight, severely impair the skin’s ability to repair UV-induced DNA damage, making individuals up to 1,000 times more likely to develop skin cancer, even with minimal sun exposure.
Weakened immunity: Those with weakened immune systems, due to taking certain medications (like immunosuppressants after organ transplants), medical conditions (such as HIV/AIDS), or chronic illnesses such as lupus, have a reduced ability to fight off abnormal cells, making them more vulnerable to developing skin cancer and other malignancies.
All these factors testify to the importance of extra vigilance, including regular skin checks, the use of daily sun protection, and prompt medical attention for any skin changes, in preventing potentially deadly diseases in those with a higher risk.
Prevention Starts With Protection: Why SPF Is Your First Line of Defense
The most effective way to reduce your risk of skin cancer is simple: protect your skin from UV rays every day. That means making sunscreen a non-negotiable part of your daily routine, not just at the beach.
But with so many products on the market, how do you know which sunscreen will truly offer the best protection for your skin?
What to Look for in an Effective Sunscreen
Not all sunscreens are created equal, and while some may provide decent sun protection, they may lack in another critical aspect, such as consistency or long-term wear.
This is why, at SunsolveMD, we created our products with the intention of setting a new standard for daily sun protection, without compromising on quality, comfort, or skin health.
Therefore, for optimal defense, choose a sunscreen with:
Broad-spectrum protection: Shields against both UVA (aging) and UVB (burning) rays, just like SunsolveMD’s ZnO+ formulas, which are designed to protect and repair your skin on a cellular level.
SPF 30 or higher: Delivers the level of protection recommended by experts, with SunsolveMD’s advanced mineral SPFs available in SPF 50 for those who want even greater peace of mind.
Water resistance: Especially important for active lifestyles, SunsolveMD’s mineral-grade micronized zinc oxide sunscreens provide a lightweight, reliable coverage that powers through your favorite outdoor activities.
Non-comedogenic and gentle formulas: Ideal for sensitive or acne-prone skin, SunsolveMD’s products are dermatologist-developed to soothe, strengthen, and support the skin barrier without irritation.
Why We Advocate for Mineral SPF And Why You Should Too (It Works for Every Skin Type)
At SunsolveMD, we’re passionate about mineral (also known as physical) SPF because we believe everyone deserves safe and effective sun protection, regardless of their skin type.
Mineral SPF is the gold standard for daily defense, having been proven time and again to offer broad-spectrum coverage without compromising skin health and comfort or harming the environment.
Therefore, we can confidently say that our commitment to mineral-based formulas is rooted in both science and our mission to support healthy, radiant skin for all.
Chemical vs. Mineral Sunscreen
Chemical sunscreens work by absorbing UV rays and converting them into heat, which is then released from the skin. These formulas often contain ingredients such as oxybenzone and avobenzone, which can sometimes cause irritation or allergic reactions, particularly in sensitive skin.
Additionally, some of these components have not only been found to accumulate in the bloodstream, but have also been noted to harm marine wildlife when worn while swimming.
Mineral sunscreens, on the other hand, use zinc oxide and titanium dioxide to form a physical barrier between the skin and UV rays. They start working immediately upon application, are less likely to irritate even the most sensitive or acne-prone skin, and are environmentally friendly, making them a smart choice for both your skin and the planet.
At SunsolveMD, we have also taken our mineral-grade, micronized formulas a step further, making them cosmetically elegant and designed to blend seamlessly, providing invisible yet powerful protection for every complexion and its unique needs.
Other Effective Ways to Lower Your Risk of Skin Cancer
Seek Shade During Peak Sun Hours
UV rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Therefore, limiting direct sun exposure during these hours can significantly reduce your risk of severe skin damage and skin cancer.
Wear Protective Clothing
Long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses provide a physical barrier against harmful rays, protecting areas that sunscreen might miss.
Avoid Short But Intense Sun Exposure
Research shows that people who experience short but intense sun exposure, such as during sunny weekends or vacations, face a significantly higher risk of melanoma and other skin cancers, especially if they live in colder climates where the skin is less adapted to UV radiation.
This pattern helps explain why Northern European countries consistently report higher rates of skin cancer than Mediterranean regions that experience steadier sun exposure throughout the year.
Therefore, preventing intense sun exposure that leads to severe sunburns and skin damage in a short period can ultimately reduce your risk of developing skin cancer in the future.
Schedule Annual Dermatologist Visits
A professional skin exam can catch early signs of skin cancer that you might overlook, especially in hard-to-see areas.
Maintain a Healthy Diet Rich in Antioxidants
Antioxidants, such as vitamins C, E, beta-carotene, and polyphenols, help stabilize reactive oxygen species and other harmful molecules, thereby reducing oxidative stress and supporting the skin’s natural repair processes.
Therefore, including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, such as berries, leafy greens, carrots, and citrus fruits, in your daily diet not only benefits your overall health but also adds an extra layer of protection against sun-related skin damage.
Keep in mind that a healthy diet is not a substitute for physical sun protection; however, it can complement other sun protection strategies for a comprehensive skin cancer prevention from the inside out.
The Bottom Line
Skin Cancer Awareness Month serves as a powerful reminder that, regardless of your age, skin tone, or background, daily sun protection is essential in preventing this common disease.
Therefore, by choosing mineral SPF and incorporating it into your routine, you’re not just protecting your skin; you’re also taking a stand against the most common cancer in the world.
At SunsolveMD, we’re here to support your journey to healthier skin and a safer future. That's why we proudly donate a portion of our proceeds to leading organizations, such as the Melanoma Research Foundation and the Skin Cancer Foundation, whose work in research, education, and advocacy is making a real difference in the fight against skin cancer.
Together, we can make SPF non-negotiable for every skin type, concern, and need, and save lives in the process.